First-generation migrant workers deserve better support in old age

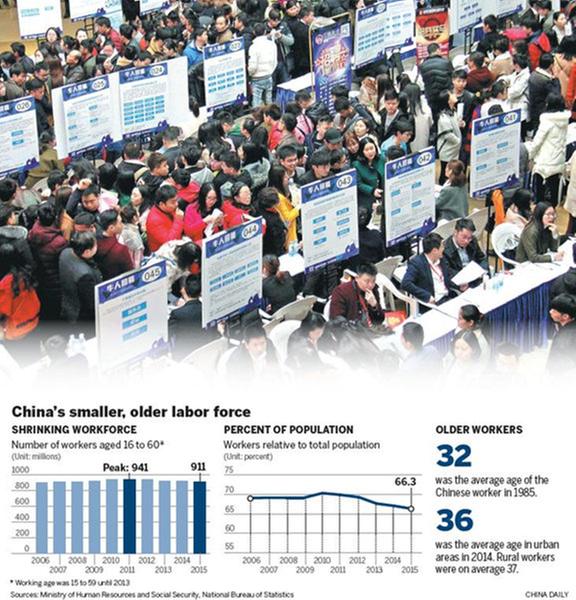
SINCE THE OPENING-UP and reform policy was launched in 1978, hundreds of millions of people from rural areas left their hometowns to work in cities. Today most of the first-generation migrant workers are in their 60s or 70s. Beijing Youth Daily comments:
Most of the first-generation migrant workers had poor education backgrounds and the jobs they took were mostly heavy physical labor, such as working on construction sites. It is fair to say that, having shouldered a large part of the physical labor in cities, they have contributed to the modernization of Chinese society.
But the social security and welfare system was far from satisfactory when they were working, so they are commonly without a liveable pension. And their wages were so low that most of them hardly have any savings.
Even after the authorities introduced a rural old pension system in 2009, according to which each rural senior citizen got only 60 yuan ($8.7) a month until this year when the pension was raised to 75 yuan a month. However, that is still too low for people to make a living. As the first-generation migrant workers reach their 60s, even 70s, how to support their lives in the rural regions poses a challenge to social stability.
Worse, when their children, or the so-called second-and third-generation migrant workers, witness this, they will ask for higher pay and refrain from doing heavy labor. Some experts say that since there is a shortage of labor, they should not give up doing physical work. Such comments are rather absurd. In order to ease the labor shortage, it is necessary to raise wages and improve the social security system, rather than just asking people to act selflessly.
China's economic development has been recognized by the whole world, and the realty prices have risen so fiercely that construction companies have got huge profits. Therefore, the State is able to improve social security and welfare for laborers, while the enterprises are able to raise their wages.
The whole of society has already reached a consensus that migrant workers should enjoy life as urban people do. Only by improving the livelihoods of first-generation migrant workers, who devoted themselves to prosperity, can the shortage of workers be solved.

































