NBS: Birthrate dropped, but more Chinese couples had second child
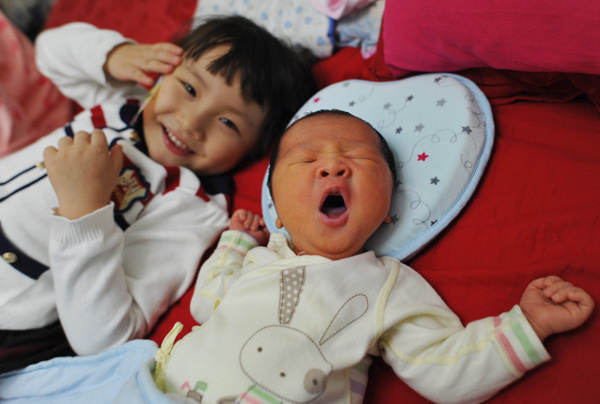


China saw an increase in the number of families who had a second child in 2017.
Some 17.23 million births were recorded nationwide last year, down by 630,000 compared with 2016, according to the National Bureau of Statistics.
Yet despite the overall decline, the country saw more than 8.82 million babies born to families that already had one child, up by 1.67 million on 2016.
The proportion of babies born as a second child in 2017 rose by 11 percentage points year-on-year to reach 51.2 percent — the highest since the 1980s, according to the data.
"The second-child boom set the tone for China's new birth demographic in 2017," said Huang Kuangshi, an associate research fellow at the China Population and Development Research Center, a government think tank. "The universal second-child policy will help sustain China's population development."
Huang attributed the increase largely to the second-child policy implemented nationwide in January 2016.
The trend was also accompanied by a record-low number of babies born as their family's first child. The figure has fluctuated slightly around 10 million since 2000, but last year it dropped to 7.24 million — less than half of all births.
Huang said the slump in first-child births was due to women of childbearing age choosing to delay pregnancies in 2017 when fertility rates peaked after the policy shift.
The annual number of first-children among newborns needs stronger monitoring and analysis, he said, adding: "If we see a consecutive decrease ... that would be alarming for the overall population development."
Huang identified two major signals from the NBS data: First, it's likely the government overestimated the number of couples who want to have more children; second, due to pressure from employment and economic insecurity, especially in urban areas, "fertility desire" is fluid and subject to change.
He called for a comprehensive review and scientific approach to evaluate the second-child policy's impact on births in 2017.
"Efforts are needed to implement real-time monitoring of births, coordinate family planning, economic and social policies, and support strategic research in population development," he added.
Wang Xiaoyu contributed to this story
- From crested ibises to pandas, China lights conservation path
- Plateau poised for world-class copper hub tag
- Xi calls for winning tough anti-graft battle
- Surging flu cases drive up demand for drug
- Nanchang funds 19 free funeral venues after tragedy
- Massive ice sculpture replicates CNS?Liaoning aircraft carrier