COVID-19 presents a terrifying new threat to people in conflict zones


If the first casualty of war is truth, the second may very well be something the entire world values highly right now: healthcare.
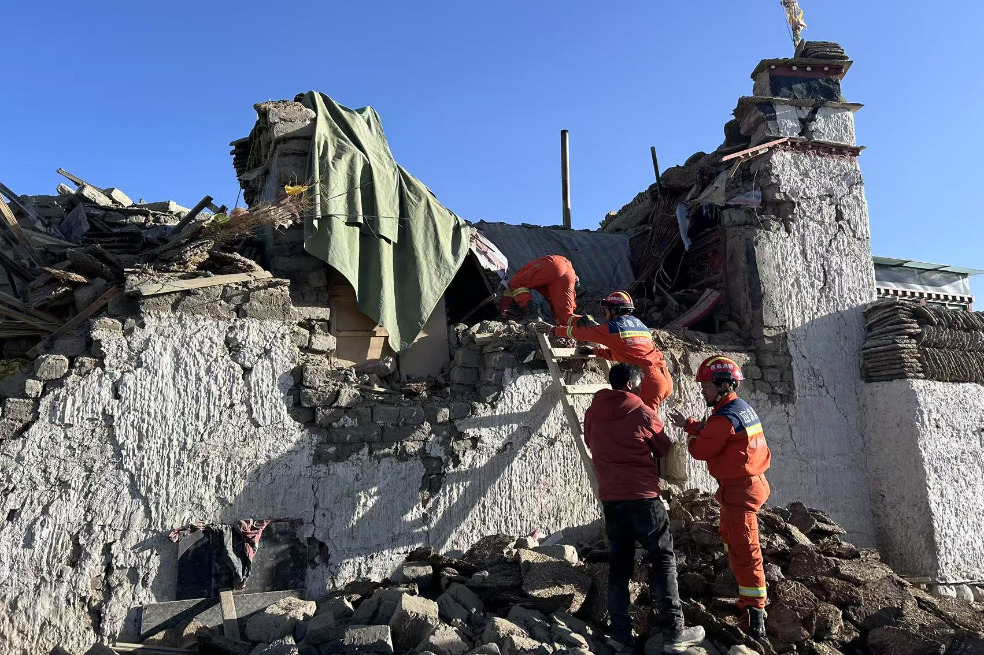
Families fleeing conflict, or currently in its crosshairs, know that medical assistance is a rare and precious privilege in war zones. Amid the terror of bombs and bullets, a functioning medical facility is a life-saving oasis, but it’s a near certainty that medical staff will be overworked and short on supplies.
This lack of medical care is what makes COVID-19’s inexorable march into conflict zones so terrifying: It’s a dramatic threat to life in places where people are often seen as nameless, faceless others. But my organization – the International Committee of the Red Cross (ICRC) – helps and gets to know real people, real families, who now lie before a violent storm.
As president of the ICRC, I’ve come to know the very hard scenes that war victims must confront. We feed the severely malnourished. We listen to survivors of sexual assault. We patch together splintered families, and we sew up grotesque war wounds.
In short, we see the world at its worst, which is why I want world leaders and governments to listen carefully: I am scared.
I am scared because the coronavirus is overwhelming even the capacities of Western nations’ advanced medical infrastructure.
I am scared that when the virus reaches the world’s under-resourced prisons, already fragile health and low medical capacity will combine to result in widespread sickness.
I am scared when COVID-19 reaches the world’s cramped refugee camps and precarious provisional shelters, where social distancing is impossible and medical resources scant.
The children, parents and especially grandparents have found that they will soon be left to fend for themselves against the disease, and that is why I’m urging governments and humanitarian groups like mine to do as much as they can to help these most vulnerable people.
This has been a necessity for a long time. Today, helping those least able to defend themselves from disease is a moral and political imperative, even – or especially – during the crippling societal and economic effects of a global health crisis. We can and must reduce the suffering this disease will cause those least able to cope.
In a 2016 study, the Rand Corporation found that Afghanistan, Haiti, Yemen and 22 countries in Africa make up the 25 countries most vulnerable to infectious disease outbreaks. The majority of the 10 most vulnerable countries were conflict zones.
The ICRC is currently carrying out a major reorientation in our assistance activities, adapting our existing work to today’s viral reality. In the medical facilities we support in countries such as Syria, Somalia and Iraq, we are increasing stocks of essential supplies and reinforcing infection prevention and control measures.
In detention facilities in more than 50 countries, the ICRC works with the authorities to strengthen medical screenings and prevention measures for new arrivals, visitors, guards and delivery personnel. We also support disinfection measures and distribute hygiene materials. We have seen such measures prevent the spread of cholera and Ebola into places of detention in Guinea, Liberia and the Democratic Republic of the Congo. We must do the same with COVID-19.
These are critical steps right now. But here is another critical step: the ICRC and others must continue to carry out non-COVID-19 work. For example, the hospitals we support in South Sudan have received more than 145 patients with gunshot wounds in recent weeks. They must be helped, too.
The sad reality is that for people living amid conflict, COVID-19 may just be one additional mortal threat. It’s for a good reason that the UN secretary general has called for a global ceasefire; humanitarian actors need all possible space to respond to the present pandemic.
Our double response to conflict and COVID-19 is extra difficult because of the vital measures taken to contain the pandemic. Travel restrictions prevent the collection of humanitarian assistance and block our teams from entering countries or delivering supplies. We’ll work to overcome these challenges, but we ask decision-makers to make exceptions for health and humanitarian work.
If helping is a moral imperative, governments and other armed actors in theaters of conflict must protect a neutral and impartial humanitarian space, not overburden it with regulations and restrictions; everyone must protect human dignity, not marginalize, exclude and stigmatize.
I’m scared that COVID-19’s assault on the world’s most vulnerable will be vicious. Time is already short, but we must work together now to reduce whatever suffering we can. Governments, belligerents and authorities must change their behavior. Viruses know no borders; the impact of a lack of response and resources for detainees and refugees may haunt the entire world.