The time of emperors


The Palace Museum and Chengde Mountain Resort highlight a collection of imported and domestic antique clocks, Wang Kaihao reports.
While the Palace Museum, China's imperial palace in Beijing from 1420 to 1911, also known as the Forbidden City, houses myriad artifacts that showcase traditional Chinese craftsmanship, it also boasts some 1,500 unique antique timepieces.
Most of these clocks, in various sizes and with dazzling ornaments, were made in Europe, mainly in the 18th and 19th centuries. Nonetheless, even in their home countries, it might be difficult to find such an ornate extravaganza of horology in one place, considering the wealth of their buyers-Qing Dynasty (1644-1911) emperors.
The emperors loved these ticking devices so much that they even took some to a mountain resort in Chengde in Hebei province, where they often spent their summers. More than 200 kilometers to the northeast of the Forbidden City, the resort was, back then, another center of governance.
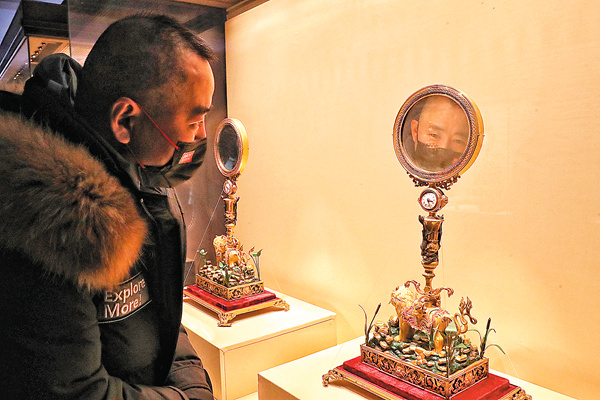
Now, with 60 antique timepieces from the two UNESCO World Heritage sites-40 from the Palace Museum and 20 from the Chengde Mountain Resort-on display in one exhibition, visitors will get a broader view of the imperial times by admiring the clocks' state-of-the-art craftsmanship.
The exhibition, Sounds of a Prosperous Age: Timepieces in the Collections of the Forbidden City and the Mountain Resort, opened in late January in the east gallery of the Hall of Heavenly Purity (Qianqing Gong) at the Palace Museum. The unprecedented display will run through May 8 before moving to Chengde.
"Timepieces are a unique and precious category in the vast royal collection of the Qing Dynasty, and maintain an important position in the world," says Guo Fuxiang, a researcher with the department of palace life and imperial rituals at the Palace Museum. "Visitors may appreciate these fine pieces and enjoy a voyage through time and artistic grandeur."
If wound, some exhibits become miniature stages, with delicate performances taking place, as decorations come "alive". Flowers rotate, birds tweet and cascades fall, presenting a magical dance. However, visitors will find the aged items silent in the exhibition, as a measure to avoid mechanical wear and tear.
Qing emperors did not treat the imported timepieces merely as tools that could tell time, but also admired them as quintessential artworks.
"The luxurious clocks would only be made when there were orders," explains Guo, also the curator of the exhibition. "To feed the Qing emperors' preference for auspicious signs, European artisans spared no effort to create a flamboyant artistic style, which could be hardly seen elsewhere."
The United Kingdom played a leading role in offering these precious timepieces to the Chinese royal court. For example, British watchmaker James Cox's name is frequently mentioned on the exhibits.
According to Guo, British clocks were mainly made of gilt brass, of which color echoed the trends of interior decoration among the UK aristocracy. They demonstrate outstanding techniques in handling gems, enamel, glass and various materials used in the making of the clocks.
Switzerland and France were two other major sources of imported clocks. Some exhibits are examples of top-tier Rococo art and metal sculpture. Following the Industrial Revolution, shapes of many French clocks were inspired by new inventions, such as locomotives, submarines and stream engines.