Bacterium discovery a boon for research
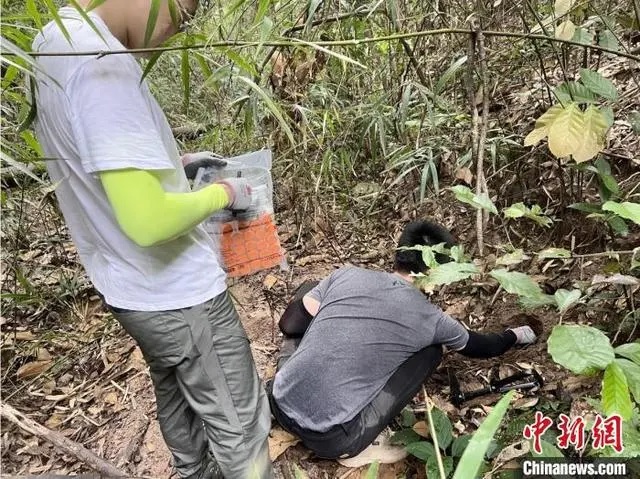


Chinese scientists have discovered a new bacterium in forest soil on Danxia Mountain in Shaoguan, Guangdong province, that could play a key role in restoring damaged ecosystems.
Li Wenjun, a microbiology professor at Sun Yat-sen University, said the bacterium, from the Danxiaibacter flavus genus, is the 41st new species discovered on Danxia Mountain and the first time this particular species has been discovered in the world.
Li led a scientific research team on a large-scale field microbial investigation and survey on the mountain earlier this year, and their discovery was published in the International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology on Oct 4.
The microbial diversity section of the biodiversity survey included a diversity assessment, collection and preservation of characteristic microbial samples in the region, and the establishment of a shared library and information database.
"The discovery is of great significance to microbiological research," said the microbiologist. Most of the members of Li's team come from Sun Yat-sen University in Guangzhou.
Danxia Mountain is rich in vegetation and dense forests and is being turned into a national park. However, the park is surrounded by mines and development projects focused on mineral resources that have damaged the surrounding ecology and environment.
"The microorganism can be utilized to restore local vegetation, protect the ecology and environment, and research and develop medicines," he told China Daily.
Li said microbial research has great potential and broad prospects, as only about 1 percent of the world's microorganisms are known.
"The other 99 percent of microorganisms need scientists, researchers and postgraduate students to unveil their mysteries through their hard work," he said.
This is the first time a Chinese scientific research team has conducted a systematic survey of microbial diversity on the mountain, a national nature reserve, which will bring new ideas to the protection of species diversity in the parks and nature reserves and generally expand the field of biological resource protection.
Previously, field investigations and surveys mainly focused on discovering new animals and plants, Li said.
The discovery will expand people's understanding of the "tree of life", and will lead to an increase in resources for genetic research, and it also has important strategic significance for the protection and development of microbial resources on Danxia Mountain, according to a statement from the Administrative Committee of Danxia Mountain.
Danxia Mountain lends its name to the Danxia landform. Covering approximately 300 square kilometers, the Danxia Basin is densely dotted with majestic Danxia landscapes. Mainly characterized by Danxia landforms, it is the largest scenic area in the province, and is a World Natural Heritage Site.
The unique landform is known as an "ecological island" that endows the subtropical evergreen broadleaf forest with rich tropical elements and creates a unique habitat for wildlife and plants.
- Nanchang funds 19 free funeral venues after tragedy
- Massive ice sculpture replicates CNS?Liaoning aircraft carrier
- China to enhance to improve carbon footprint
- Experts advocate vaccinations to combat flu cases
- Singer Lu Han apologizes for inappropriate behavior
- Xi stresses winning tough, protracted and all-out battle against corruption