Africa seeks to make climate needs known on global stage


Experts want continent to focus on sustainable farming while it grapples with extreme weather events
In the year following Africa's hosting of the 27th United Nations climate summit, more commonly referred to as COP27, held in Egypt in 2022, the continent has endured a run of lethal and unprecedented extreme weather events.
In September, Libya hit global headlines when Storm Daniel made landfall, causing severe weather conditions, including strong winds and sudden heavy rainfall that affected several areas in the country. Massive floodings killed more than 4,300 people, and more than 8,500 are still missing, according to the United Nations Children's Fund.
Even though Libya's floods were among the few African climate extremes that made global headlines last year, many other deadly and life-threatening events in Africa failed to gain international news coverage.
The Horn of Africa has seen almost three years of some of the worst drought conditions in history, said the Famine Early Warning Systems Network, a global provider of early warning and analysis on acute food insecurity. Ethiopia and Somalia have experienced five failed rainy seasons since late 2020, which have displaced 1.4 million Somalis and killed 3.8 million livestock.
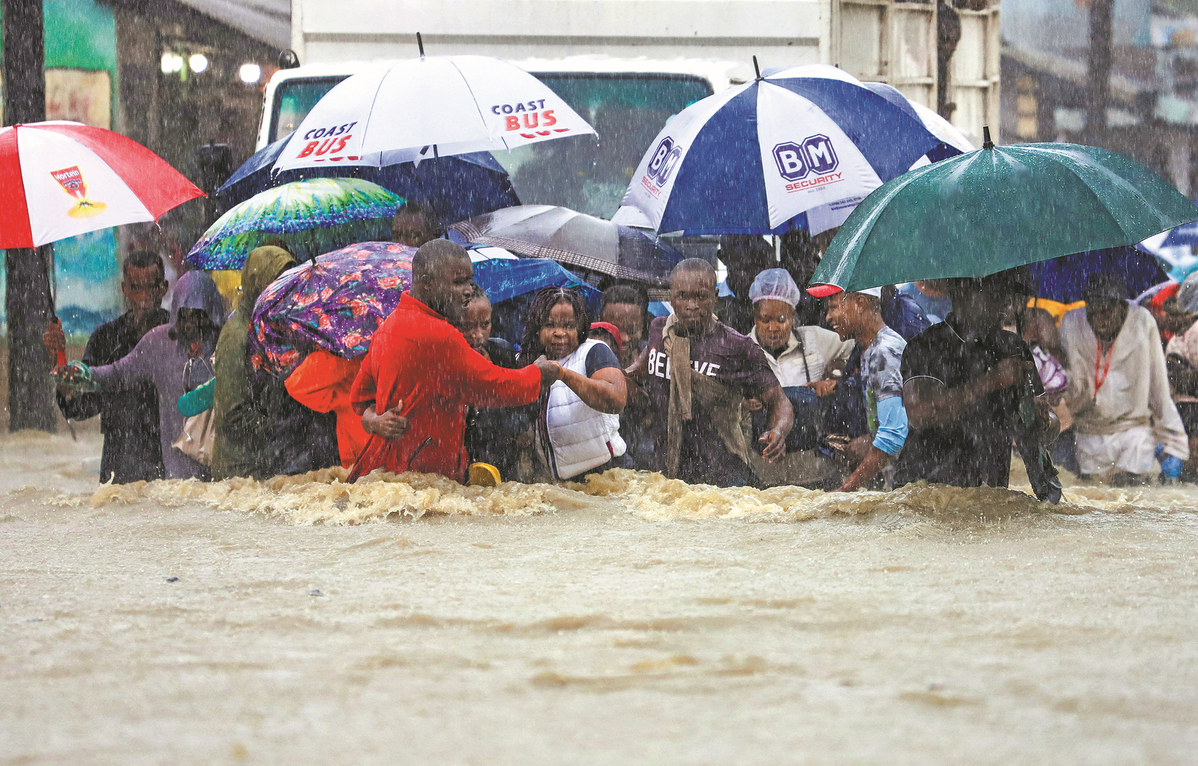
This period of extreme drought was followed by the El Nino-induced heavy rains and flash flooding that killed hundreds in Ethiopia, Kenya and Somalia last year, the United Nations said. The deluge swamped more than 1,000 hectares of cropland in Ethiopia and Somalia, challenging the agricultural economies in the two countries where more than 65 percent of the population relies on farming and much of the region's farmland relies on rainfall for irrigation.
Kilion Nyambuga, a research and planning expert involved in the resettlement of slum dwellers in Kenya, said Africa is responsible for only a fraction of global emissions but is suffering disproportionately from climate change.
"The fact that Africa is continuously facing the extreme effects of climate change despite the continent's low emissions is harming food security, ecosystems and economies while fueling displacement, migration and worsening the threat of conflict over dwindling resources," he said.
Emissions of carbon dioxide per person in Africa in 2021 were 1.04 metric tons, standing in stark contrast to the global average, which is more than four times as high, said a report published by the World Meteorological Organization in September.
The report, called "State of the Climate in Africa 2022", said the rate of temperature increase across Africa has accelerated in recent decades, with weather and climate-related hazards becoming more severe. Yet, financing for climate adaptation is a drop in the ocean of what is needed.
Nyambuga said the global approach, which seems fixated on mitigation, neglects Africa's pressing need for adaptation financing and loss and damage compensation. The decision by African countries to host the inaugural Africa Climate Summit in Kenya's capital Nairobi in September 2023, was timely and "a plus for the African Union", he said.
Alex Mugambi, chair of the Environmental Institute of Kenya, said the African Climate Summit was a success, highlighting the adoption of the Nairobi Declaration, a comprehensive document that outlines Africa's vision, priorities, and demands for climate action and finance.
"The declaration call was a win for Africa for calling for a new global financial deal with fit-for-purpose financing instruments and products to serve Africa's specific growth goals," Mugambi said.